 |
| Diseases 1 Chart |
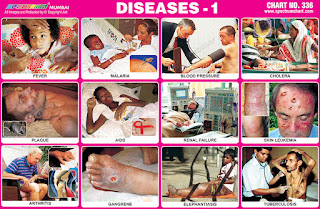
Spectrum Chart - 336 : Diseases 1
1. Fever – A fever is when a person's
body temperature is hotter than 37.5 degrees Celsius (99.5
Fahrenheit). Normal body temperature for humans varies based on a
variety of factors, including age and level of physical activity. A
fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from the not
serious to potentially serious. This includes viral, bacterial and
parasitic infections such as the common cold, urinary tract
infections, meningitis, malaria and appendicitis among others.
2. Malaria – Malaria is an infectious
disease caused by a parasite it is spread by the bite of an infected
mosquito. People catch malaria when the parasite enters the blood.
The parasite causes a deadly infection which kills many people each
year. Malaria is treated with antimalarial medications, the ones used
depends on the type and severity of the disease.
3. Blood Pressure - Blood pressure is a
measurement used in medicine. In the body, the arteries carry blood
away from the heart. As blood travels through the arteries, it
presses against the walls of the arteries. Blood pressure measures
how hard the blood is pushing against the walls of the arteries.
Blood pressure that is low due to a disease state is called
hypotension and pressure that is consistently high is hypertension.
Long term hypertension is a risk factor for many diseases, including
heart disease, stroke and kidney failure.
4. Cholera – Cholera is an infection of
the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom
is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting
and muscle cramps may also occur. Cholera may be life-threatening,
prevention of the disease is normally straightforward if proper
sanitation practices are followed. In developed countries, due to
nearly universal advanced water treatment and sanitation practices,
cholera is no longer a major health threat.
5. Plague – Plague is an infectious
disease that is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Depending on
lung infection, or sanitary conditions, plague can be spread in the
air, by direct contact or very rarely by contaminated under cooked
food. The symptoms of plague depend on the concentrated areas of
infection in each person bubonic plague in lymph nodes, septicemic
plague in blood vessels, pneumonic plague in lungs. It is treatable
if detected early. Plague is still relatively common in some remote
parts of the world.
6. Aids - Human immunodeficiency virus
infection and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a
spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV is transmitted by three main routes
sexual contact, significant exposure to infected body fluids or
tissues and from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery or
breastfeeding. HIV/AIDS is diagnosed via laboratory testing and then
staged based on the presence of certain signs or symptoms. In many
areas of the world, a third of HIV carriers only discover they are
infected at an advanced stage of the disease when AIDS or severe
immunodeficiency has become apparent.
7. Renal Failure - Renal failure is a
medical condition of impaired kidney function in which the kidneys
fail to adequately filter metabolic wastes from the blood. The two
main forms are acute kidney injury, which is often reversible with
adequate treatment and chronic kidney disease, which is often not
reversible. In both cases, there is usually an underlying cause.
Renal failure is mainly determined by a decrease in glomerular
filtration rate, which is the rate at which blood is filtered in the
glomeruli of the kidney.
8. Skin Leukemia - Skin leukemia is a
group of cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in
high numbers of abnormal white blood cells. These white blood cells
are not fully developed and are called blasts or leukemia cells.
Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising problems, feeling tired,
fever and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due
to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood
tests or bone marrow biopsy.
9. Arthritis - Arthritis is a form of
joint disorder that involves inflammation in one or more joints.
There are over 100 different forms of arthritis. Pain, which can vary
in severity, is a common symptom in virtually all types of arthritis.
Other symptoms include swelling, joint stiffness and aching around
the joint. There is no known cure for either rheumatoid or
osteoarthritis. Treatment options vary depending on the type of
arthritis and include physical therapy, lifestyle changes, orthopedic
bracing and medications.
10. Gangrene – Gangrene is a serious
medical condition that causes the decay and death of body tissue,
usually in the extremities such as the fingers, hands, toes, and
feet. The two main types of gangrene are dry gangrene and wet
gangrene. A third less common type is a form of wet gangrene known as
gas gangrene. Gangrene is caused by a critically insufficient blood
supply or infection. It is associated with diabetes and long-term
tobacco smoking. The best treatment for gangrene is revascularization
of the afflicted organ, which can reverse some of the effects of
necrosis and allow healing. Other treatments include antibiotic
therapy, wound care, debridement and surgical amputation.
11. Elephantiasis – Elephantiasis is
caused by parasitic worms of the roundworm family. Many cases of the
disease have no symptoms. Some people however, develop the syndrome
of elephantiasis which may include severe swelling in the arms, legs
or genitals. The changes to the body can cause social and economic
problems for the affected person.
12. Tuberculosis – Tuberculosis (TB) is
an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium
tuberculosis (MTB). Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but can
also affect other parts of the body. The classic symptoms of active
TB are a chronic cough with blood-containing sputum, fever, night
sweats and weight loss. Tuberculosis prevention and control efforts
rely primarily on the vaccination of infants and the detection and
appropriate treatment of active cases.

No comments:
Post a Comment