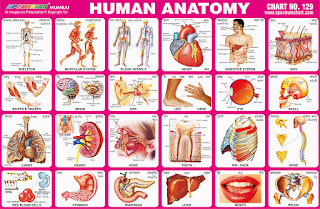
Skeleton – Skeleton is
the hard structure that supports the body of a living thing.
Skeleton supports the skin, muscle and tissue, and all the organs
that are inside the body. The skeleton protects important internal
organs like the brain, heart and lungs.
Muscular System - Muscular
system is one of the major systems in our body. Its main purpose is
to produce movement. Muscle is a tissue in human bodies. Muscles help
us to move our body parts.
Blood Vessels -
Blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that
transports blood throughout the human body. There are three major
types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away
from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of
water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues; and the
veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back toward the heart.
Heart – Heart is a
muscular organ in humans, which pumps blood through the blood
vessels of the circulatory system. Heart is located in the middle
compartment of the mediastinum in the chest. The human heart has
four chambers or closed spaces, the four chambers are two atria and
two ventricles.
Digestive System -
Digestive system consists of organs like tongue, salivary glands,
liver, pancreas and gallbladder. The digestive system is responsible
for breaking down food we eat into smaller components so that
nutrients can be easily absorbed by the body and the waste
discarded.
Skin – Human skin is the
covering or integument, of the body’s surface that both provides
protection and receives sensory stimuli from the external
environment.The skin consists of three layers of tissue, (i) the
epidermis, an outermost layer that contains the primary protective
structure, the stratum corneum, (ii) the dermis, a fibrous layer
that supports and strengthens the epidermis and (iii) the subcutis,
a subcutaneous layer of fat beneath the dermis that supplies
nutrients to the other two layers and that cushions and insulates
the body.
Biceps – In human
anatomy, the biceps brachii, commonly known as the biceps, is a
two-headed muscle that lies on the upper arm between the shoulder
and the elbow. Biceps works across three joints. The most important
of these functions is to supinate the forearm and flex the elbow.
Triceps - Triceps brachii
muscle, commonly known as triceps, is the large muscle on the back
of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It is the muscle principally
responsible for extension of the elbow joint. The triceps
straightens the elbow pulls against the biceps and brachialis
muscles.
Brain – Brain is an organ
that serves as the centre of the nervous system. For humans, it is
the source of consciousness. The brain also controls basic autonomic
body actions, like breathing, digestion, heartbeat, that happen
automatically.
Ear - The ear is the organ
of hearing. Ears convert sound waves into nerve impulses that are
sent to the brain. While your ears pick up the sound, it is your
brain that does the hard work of making sense of it all.
Leg - Human leg, is the
entire lower extremity of the human body, including the foot,thigh
and even the hip or gluteal region. Legs are used for standing,
walking, jumping, running, dancing and similar activities and
constitute a significant portion of a person's mass.
Hand - A hand is the part
of the body at the end of an arm. Humans have two hands. Each hand
has four fingers and a thumb. On the inside of the hand is the palm.
Among humans, the hands play an important function in body language
and sign language.
Eye - Eyes are the organs
of vision. Eyes detect light and allow us to see. The part of the
eye that allows us to focus on different things in known as the
lens, it changes shapes so we can focus on objects at various
distances.
Skull - The human skull is
the bony structure that forms the head in the human skeleton. It
supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the
brain.
Lungs – The lungs are the
primary organs of respiration in humans. Humans have two lungs, a
right lung and a left lung. They are situated within the thoracic
cavity of the chest. The right lung is bigger than the left, which
shares space in the chest with the heart. The lungs together weigh
approximately 1.3 kilograms (2.9 lb), and the right is heavier.
Kidney – Kidneys are two
organs in the abdomen of vertebrates that are shaped like beans.
They are part of the urinary system. They serve the body as a
natural filter of the blood, and remove water-soluble wastes which
are diverted to the bladder. In producing urine, the kidneys excrete
nitrogenous wastes such asure and ammonium.
Nose - A nose is a body
part which allows humans to breathe air & smell things. It
filters the air breathed in, removing dust, germs and irritants. It
warms and moistens the air to keep the lungs and tubes that lead to
them from drying out.
Tooth - The human teeth
function is mechanically breaking down items of food by cutting and
crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digestion. There are
four different types of teeth, namely incisors, canines, molars and
premolars.
Rib Cage – The rib cage is
a part of the skeleton of humans. It is made up of curved bones. The
rib cage is found in the chest area. It protects a persons internal
organs from damage. Most humans have 12 pairs of rib bones with one
from each pair on each side of the chest. The bones are also filled
with bone marrow, full of calcium and protein.
Spine – The spine is a
column of vertebrae in the back part of the torso (upper body). It
is also called the backbone or vertebral column. In the human spine
there are normally thirty-three vertebrae.
DNA – DNA, short for
deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that contains the genetic
code of organisms. DNA is inherited by children from their parents.
This is why children share traits with their parents, such as skin,
hair and eye colour. The DNA in a person is a combination of the DNA
from each of their parents.
White Blood Cells - White
blood cells (WBCs), also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the
cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body
against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. The number of
white blood cells increases when a person is fighting infection or
disease and decrease when a person is healthy.
Red Blood Cells - Red blood
cells, are cells in the blood which transport oxygen. Red blood
cells are red because they have haemoglobin in them. The red blood
cells are develop in the bone marrow and circulate for about 100–120
days in the body before their components are recycled by
macrophages. Approximately a quarter of the cells in the human body
are red blood cells. Nearly half of the blood's volume (40% to 45%)
is red blood cells.
Stomach - Stomach is part
of the digestive system. The stomach is the third stage in the
digestive process. It holds food after ingestion. Food in the
stomach then passes through to the small intestine where most of the
food's nutrition are absorbed.
Pancreas – Pancreas is an
organ that makes hormones and enzymes to help digestion. The
pancreas helps break down carbohydrates, fats and proteins. The
pancreas is behind the stomach and is on the left side of the human
body. The
pancreas belongs to two systems of the body: the digestive system
for its role in breaking down nutrients and the endocrine system for
producing hormones.
Liver – The liver is an
organ in the abdomen. It is part of the gastrointestinal system. The
liver is a gland and plays a major role in metabolism with numerous
functions in the human body, including regulation of glycogen
storage, decomposition of red blood cells, plasma protein synthesis,
hormone production, and detoxification.
Mouth - Mouth is an opening
in the face, is the first part of the alimentary canal (digestive
system). It is the place where the chewing of food occurs. The mouth
has teeth to help chew the food.
Pelvis – Pelvis is either
the lower part of the trunk of the human body between the abdomen
and the thighs. Its primary functions are to bear the weight of the
upper body when sitting and standing. Its secondary functions are to
contain and protect the pelvic and abdominopelvic viscera, providing
attachment for external reproductive organs and associated muscles
and membranes.

No comments:
Post a Comment